Yes, Coreg (carvedilol) effectively lowers blood pressure. It’s a beta-blocker and alpha-blocker, meaning it works on multiple systems in your body to achieve this.
Coreg’s blood pressure-lowering action stems from its ability to relax blood vessels, reducing the resistance your heart faces when pumping blood. This reduction in resistance directly translates to lower blood pressure readings. Studies show a significant reduction in both systolic and diastolic pressure in patients taking Coreg.
However, remember that Coreg’s effectiveness varies from person to person. Your doctor will consider your specific health conditions and other medications you take when determining the appropriate dosage and monitoring your response. Regular blood pressure checks are crucial for personalized adjustment.
Important Note: Coreg carries potential side effects. Common ones include dizziness, fatigue, and nausea. Always discuss potential side effects and any concerns with your healthcare provider before starting or changing your medication regimen. They can guide you through safe and effective management of your blood pressure.
- Does Coreg Lower Blood Pressure?
- How Coreg Lowers Blood Pressure
- Understanding Coreg Dosage and Side Effects
- Monitoring Your Blood Pressure
- What is Coreg (carvedilol)?
- How Coreg Works to Reduce Blood Pressure
- Beta-Blockade: Slowing the Heart
- Alpha-Blockade: Relaxing Blood Vessels
- Important Considerations
- Typical Dosage and Administration of Coreg
- Side Effects Associated with Coreg Use
- Potential Drug Interactions with Coreg
- Who Should Not Take Coreg?
- Long-Term Use of Coreg and Blood Pressure Management
- When to Consult a Doctor Regarding Coreg and Blood Pressure
Does Coreg Lower Blood Pressure?
Yes, Coreg (carvedilol) effectively lowers blood pressure. It’s a beta-blocker and alpha-blocker, meaning it works in multiple ways to reduce blood pressure.
How Coreg Lowers Blood Pressure
Coreg reduces the heart’s workload by slowing the heart rate and relaxing blood vessels. This decreased workload translates directly into lower blood pressure readings. It’s important to note that Coreg’s effect varies depending on individual factors.
Understanding Coreg Dosage and Side Effects
Your doctor will determine the appropriate dosage based on your health status and blood pressure levels. Common side effects include dizziness, fatigue, and nausea. These often lessen as your body adjusts. Always report any concerns to your physician.
| Side Effect | Frequency | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Dizziness | Common | Report to doctor; may subside over time. |
| Fatigue | Common | Rest as needed; discuss with doctor. |
| Nausea | Common | Report to doctor; may require dosage adjustment. |
Monitoring Your Blood Pressure
Regularly monitor your blood pressure as directed by your doctor. This helps track the medication’s effectiveness and allows for timely adjustments if necessary. Consistent monitoring is key to managing your hypertension effectively.
What is Coreg (carvedilol)?
Coreg is a prescription medication containing carvedilol, a beta-blocker used to treat several conditions. It works by blocking the effects of adrenaline, slowing your heart rate and relaxing blood vessels, which lowers blood pressure.
Doctors prescribe Coreg for hypertension (high blood pressure), angina (chest pain), heart failure, and sometimes following a heart attack. It’s available in various strengths, and your doctor determines the appropriate dosage based on your individual needs and health.
Common side effects include dizziness, fatigue, and nausea. More serious side effects, though less common, require immediate medical attention. Always inform your doctor about all medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, to avoid potential interactions.
Remember, Coreg is a powerful medication. Strictly adhere to your doctor’s instructions regarding dosage and administration. Regular checkups are crucial to monitor your response to the treatment and adjust the dosage if needed. Do not stop taking Coreg suddenly without consulting your physician.
How Coreg Works to Reduce Blood Pressure
Coreg, or carvedilol, lowers blood pressure through two primary mechanisms: blocking beta-adrenergic receptors and blocking alpha-adrenergic receptors. Beta-blockers like Coreg reduce the heart’s workload by slowing its rate and decreasing the force of its contractions. This directly translates to lower blood pressure.
Beta-Blockade: Slowing the Heart
By blocking beta-receptors, Coreg prevents the hormones adrenaline and noradrenaline from increasing heart rate and contractility. This reduces the pressure exerted against artery walls, leading to lower blood pressure. The effect is a slower, more controlled heartbeat.
Alpha-Blockade: Relaxing Blood Vessels
Coreg also blocks alpha-adrenergic receptors. This action causes blood vessels to dilate, reducing resistance to blood flow. Wider blood vessels allow blood to flow more easily, further contributing to reduced blood pressure. This dual action makes Coreg particularly effective for managing hypertension.
Important Considerations
While Coreg is effective, its use should be guided by a physician. Individual responses vary, and careful monitoring is necessary. Side effects should be discussed with your doctor. Proper dosage is paramount for optimal results and minimal side effects.
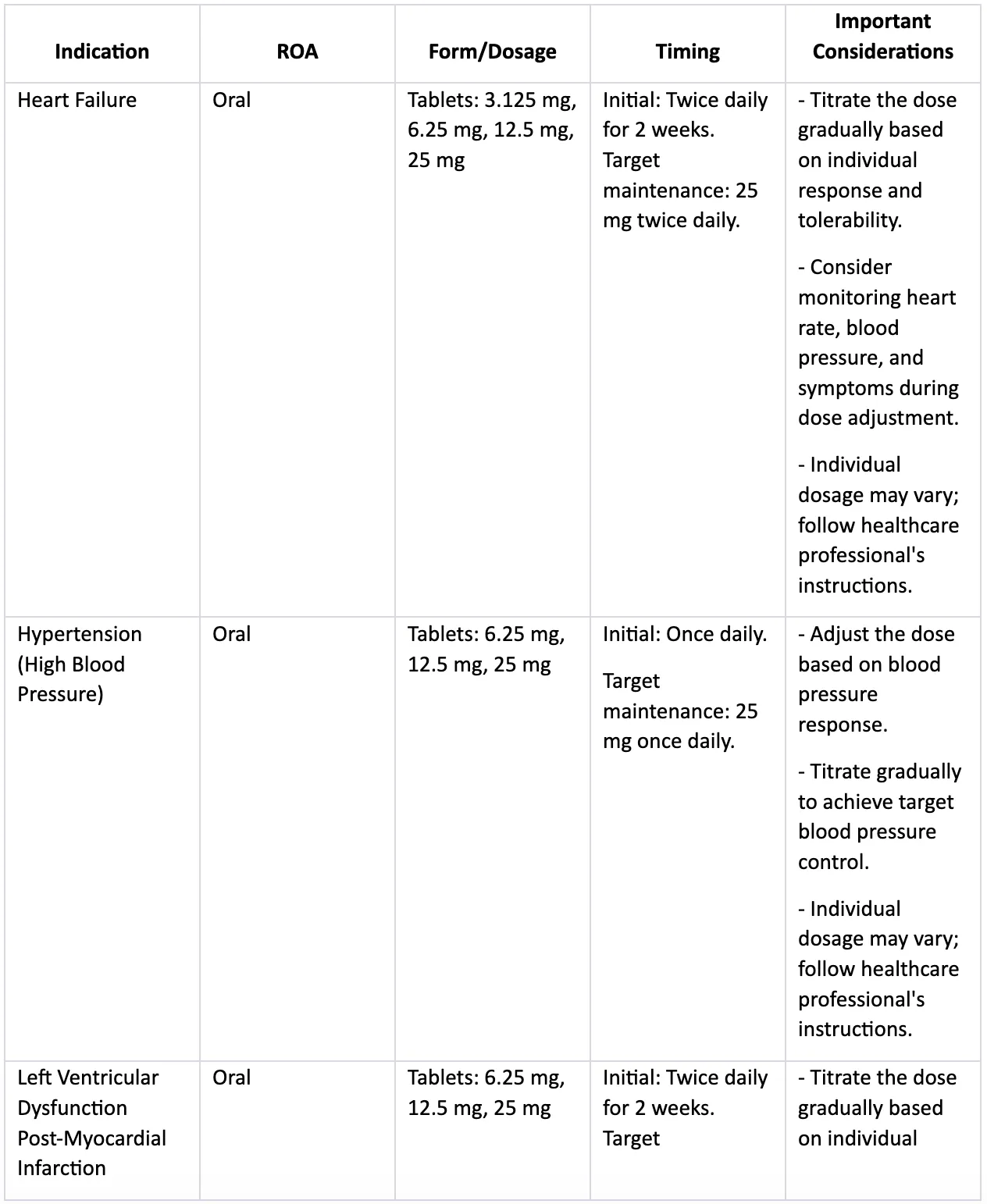
Typical Dosage and Administration of Coreg
Coreg (carvedilol) dosage depends heavily on your individual needs and response to treatment. Your doctor will carefully determine the appropriate starting dose and adjust it gradually as needed. Don’t adjust your dosage without consulting your physician.
Generally, treatment begins with a low dose and is slowly increased over several weeks. Here’s a typical regimen:
- For hypertension (high blood pressure): Treatment often starts with 3.125 mg twice daily. Your doctor may gradually increase this to a maximum of 50 mg twice daily, depending on your response and tolerance.
- For heart failure: The starting dose is usually 3.125 mg twice daily. This may be increased gradually to a maximum daily dose of 25 mg twice daily, again based on individual patient response and tolerance.
Coreg is typically administered orally, twice daily, with or without food. Always take your medication exactly as prescribed. Missed doses should be taken as soon as possible, unless it’s almost time for the next dose – then skip the missed dose and continue with your usual schedule. Never double the dose to make up for a missed one.
It’s important to note that this information is for general knowledge only and should not replace advice from your healthcare provider. Individual dosages may vary significantly depending on your health condition, other medications you’re taking, and your doctor’s assessment.
- Always consult your doctor before starting, stopping, or changing your Coreg dosage.
- Report any side effects immediately to your doctor.
- Regularly monitor your blood pressure as directed by your doctor.
Side Effects Associated with Coreg Use
Coreg, like many medications, can cause side effects. Common side effects include dizziness, fatigue, and nausea. These are often mild and temporary, but you should report them to your doctor if they persist or worsen.
Less common, but still possible, side effects involve slower heart rate (bradycardia), low blood pressure (hypotension), and shortness of breath. Severe allergic reactions, although rare, can manifest as skin rash, itching, or swelling. In such cases, seek immediate medical attention.
Changes in mood, such as depression or anxiety, have also been reported. If you experience significant changes in your mental state while taking Coreg, contact your doctor promptly. Your doctor can discuss potential adjustments to your medication or recommend additional support.
Gastrointestinal issues, including constipation and diarrhea, are also possibilities. Maintaining a healthy diet and hydration may help mitigate these effects. If these symptoms are severe or persistent, contact your healthcare provider.
This information is not exhaustive. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist for a complete list of potential side effects and discuss any concerns you may have.
Potential Drug Interactions with Coreg
Coreg (carvedilol) can interact with several medications, potentially affecting blood pressure control or causing adverse effects. Always inform your doctor about all medications you take, including over-the-counter drugs, supplements, and herbal remedies.
Drugs that may increase Coreg’s effects, lowering blood pressure excessively: These include other blood pressure medications like ACE inhibitors (e.g., lisinopril), ARBs (e.g., valsartan), diuretics (e.g., furosemide), and calcium channel blockers (e.g., amlodipine). Your doctor may need to adjust dosages to avoid dangerously low blood pressure.
Drugs that may decrease Coreg’s effectiveness: Rifampin, a medication used to treat tuberculosis, can reduce Coreg’s levels in your body. Your doctor might need to prescribe a higher Coreg dose or a different medication.
Specific examples of potentially problematic interactions: Combining Coreg with certain antidepressants (like tricyclic antidepressants or MAO inhibitors) can increase the risk of low blood pressure and fainting. Similarly, using Coreg with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or naproxen can reduce Coreg’s effectiveness.
Important Note: This is not an exhaustive list. This information is for general knowledge and does not substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting, stopping, or changing any medication, especially when taking Coreg.
Who Should Not Take Coreg?
Coreg (carvedilol) isn’t for everyone. Avoid Coreg if you have a history of severe heart block or bradycardia (slow heart rate). This medication can further slow your heart, leading to potentially dangerous complications.
Similarly, avoid Coreg if you experience severe asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Coreg can worsen breathing problems in susceptible individuals.
Severe liver disease also necessitates caution. Your doctor should carefully consider the risks and benefits before prescribing Coreg, as liver function affects its metabolism and elimination from your body.
If you’re currently taking medications to lower your blood pressure or heart rate, talk to your doctor. Interactions can occur, potentially causing dangerously low blood pressure or heart rate.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding also require careful consideration. The potential benefits must outweigh the possible risks to the developing fetus or nursing infant. Consult your doctor for appropriate guidance.
Finally, always inform your doctor of all your medical conditions and medications, including over-the-counter drugs and herbal supplements. This allows for a proper assessment of potential drug interactions and contraindications.
Long-Term Use of Coreg and Blood Pressure Management
Maintaining consistent blood pressure control with Coreg requires ongoing monitoring and adjustments. Regular check-ups with your doctor are key.
Here’s what you should expect and do:
- Regular Blood Pressure Monitoring: Your doctor will schedule regular appointments to check your blood pressure and assess your response to Coreg. This allows for timely adjustments to your dosage or treatment plan if needed.
- Dosage Adjustments: Your initial Coreg dose might need changes as your body adapts. Don’t adjust your dosage yourself; always consult your doctor.
- Potential Side Effects: Be aware of potential side effects like dizziness, fatigue, or nausea. Report any concerning symptoms immediately to your doctor. They might adjust the dosage or suggest alternative strategies.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Coreg is more effective when combined with healthy lifestyle choices. This includes regular exercise, a balanced diet low in sodium, and maintaining a healthy weight.
Long-term success depends on consistent adherence to your treatment plan. This includes taking Coreg as prescribed and actively participating in your healthcare management.
- Medication Adherence: Take Coreg exactly as prescribed, even if you feel well. Skipping doses can disrupt blood pressure control.
- Open Communication: Maintain open communication with your doctor about any concerns, changes in your health, or difficulties adhering to your treatment. Don’t hesitate to ask questions.
- Monitoring for Complications: Long-term use of Coreg may increase the risk of certain complications. Your doctor will monitor for these and implement strategies to manage them if necessary.
Remember, consistent effort and collaboration with your healthcare provider are fundamental to successful long-term blood pressure management using Coreg.
When to Consult a Doctor Regarding Coreg and Blood Pressure
Schedule an appointment immediately if you experience dizziness or fainting. These could signal dangerously low blood pressure.
Contact your doctor if you notice a persistent, significant cough. This is a potential side effect of Coreg.
Report any swelling in your ankles, feet, or legs. Fluid retention can be a serious complication.
Seek medical advice if you develop unusual fatigue or shortness of breath. These symptoms warrant investigation.
Inform your doctor about any new or worsening heart problems, such as chest pain or irregular heartbeat.
Regularly discuss your blood pressure readings with your doctor, especially if they remain high despite taking Coreg. Consistent monitoring is key to effective treatment.
Always consult your doctor before making any changes to your Coreg dosage or stopping the medication altogether. Sudden cessation can be harmful.
Report any new medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, as they can interact with Coreg and affect your blood pressure.
If you experience any unexpected or concerning symptoms, regardless of their severity, contact your doctor immediately for guidance.