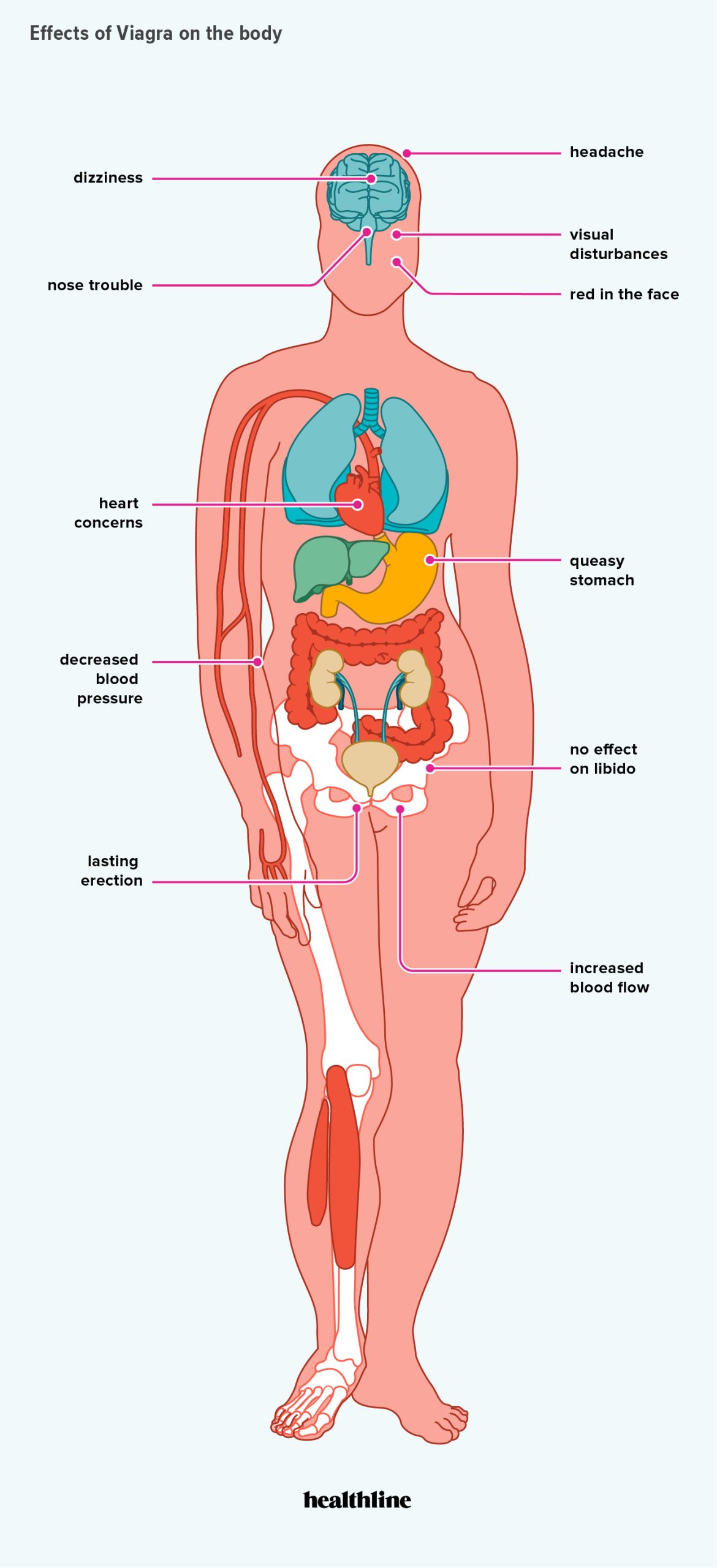
Generic Viagra, containing sildenafil, can indeed lower blood pressure. This effect is due to sildenafil’s inhibition of phosphodiesterase-5, an enzyme that affects blood vessel relaxation. The magnitude of this blood pressure reduction varies depending on the individual and the dose taken.
For men with pre-existing hypertension or those taking other blood pressure medications, this interaction can be significant. Consult your physician before taking sildenafil, particularly if you’re already on nitrates or alpha-blockers, as the combination can cause a dangerous drop in blood pressure. Your doctor can assess your specific health profile and determine the appropriate course of action.
Specific recommendations include: Always disclose your complete medical history to your doctor, including all medications and supplements. Never exceed the prescribed dosage of sildenafil. Regular monitoring of your blood pressure is advisable, especially after starting or changing your sildenafil dosage. Be aware of potential side effects, such as headaches, flushing, and nasal congestion, and report any concerning symptoms to your healthcare provider immediately.
Remember, this information is for educational purposes and does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor before starting any new medication, including generic Viagra, to ensure its safe and appropriate use based on your individual health needs.
- Does Generic Viagra Lower Blood Pressure?
- Understanding the Interaction
- Managing Blood Pressure Concerns
- Precautions and Recommendations
- When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
- Viagra’s Mechanism of Action and Potential Blood Pressure Effects
- Nitrates and Blood Pressure
- Other Blood Pressure Interactions
- Individual Variation
- Individuals at Higher Risk of Blood Pressure Changes with Viagra
- Specific Health Conditions Increasing Risk
- Medication Interactions
- Managing Blood Pressure While Taking Generic Viagra
- Lifestyle Changes
- Medication Management
- Seek Medical Attention
- Hydration
Does Generic Viagra Lower Blood Pressure?
Generic Viagra (sildenafil) can lower blood pressure, especially when combined with nitrates or certain other medications. This effect is due to sildenafil’s mechanism of action, which involves relaxing blood vessels.
Understanding the Interaction
The interaction is significant because nitrates, commonly used to treat angina (chest pain), also relax blood vessels. Combining these drugs can cause a significant drop in blood pressure, potentially leading to dizziness, fainting, or even more serious complications.
- Nitrates: Avoid using Viagra with any form of nitrate medication, including nitroglycerin.
- Alpha-blockers: Similar blood pressure-lowering effects can occur when combining Viagra with alpha-blockers (used for high blood pressure and enlarged prostate).
- Other Medications: Consult your doctor about all medications you’re taking, including those prescribed and over-the-counter, before using Viagra.
Managing Blood Pressure Concerns
If you have pre-existing low blood pressure, heart conditions, or take medications that affect blood pressure, talk to your doctor before using Viagra. They can assess your individual risk and advise on appropriate dosage or alternative treatments.
Precautions and Recommendations
- Always follow your doctor’s prescribed dosage.
- Report any unusual symptoms, such as dizziness or lightheadedness, immediately.
- Avoid alcohol consumption while using Viagra, as it can exacerbate blood pressure-lowering effects.
- Regular blood pressure monitoring is advisable, especially when initiating treatment with Viagra.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Seek immediate medical help if you experience severe chest pain, prolonged dizziness, or fainting after taking Viagra. These can be signs of serious cardiovascular complications.
Viagra’s Mechanism of Action and Potential Blood Pressure Effects
Viagra, or sildenafil, primarily works by inhibiting phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5), an enzyme that breaks down cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP). Increased cGMP levels relax blood vessels in the penis, facilitating improved blood flow and erections. This vasodilation, however, isn’t limited to the penis; it affects blood vessels throughout the body.
Nitrates and Blood Pressure
Simultaneous use of Viagra and nitrates, medications commonly prescribed for angina (chest pain), poses a significant risk. Nitrates also cause vasodilation, and their combined effect can lead to a dramatic and potentially dangerous drop in blood pressure, causing dizziness, fainting, or even heart attack. Consult your doctor before taking Viagra if you use nitrates.
Other Blood Pressure Interactions
Viagra can interact with other medications affecting blood pressure, albeit typically to a lesser extent than with nitrates. Alpha-blockers, often used to treat high blood pressure and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), can enhance Viagra’s vasodilating effects. This combination may cause orthostatic hypotension (a sudden drop in blood pressure upon standing). Individuals taking alpha-blockers should discuss Viagra use with their physician. Additionally, some blood pressure medications may be affected by liver metabolism which is also how Viagra is processed.
Individual Variation
The effect of Viagra on blood pressure varies significantly between individuals. Factors such as age, overall health, and other medications influence the response. Regular monitoring of blood pressure, particularly after starting Viagra, is advisable, especially for those with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions. Always inform your doctor about all medications you are taking.
Individuals at Higher Risk of Blood Pressure Changes with Viagra
Certain individuals experience a greater likelihood of blood pressure fluctuations when using Viagra. Men with pre-existing cardiovascular disease are particularly vulnerable. This includes those with angina, heart failure, or a history of heart attack or stroke. Their bodies may react more sensitively to Viagra’s vasodilating effects, potentially leading to a significant drop in blood pressure. This risk is heightened if they also take nitrates, medications commonly used to treat angina. Combining these can cause a dangerous drop in blood pressure, even resulting in fainting or a more serious medical event.
Specific Health Conditions Increasing Risk
High blood pressure (hypertension) itself increases susceptibility to adverse blood pressure changes with Viagra. Similarly, individuals with low blood pressure (hypotension) are at increased risk of experiencing dangerously low blood pressure. Those with severe liver or kidney disease may also experience amplified effects due to impaired medication metabolism and excretion. Conditions affecting blood vessel health should also be considered, including peripheral artery disease.
Medication Interactions
Beyond nitrates, other medications can interact negatively with Viagra, potentially affecting blood pressure. For example, some alpha-blockers used to treat high blood pressure or benign prostatic hyperplasia can exacerbate the blood pressure-lowering effects of Viagra. Always inform your doctor about all medications and supplements you are currently taking before starting Viagra to prevent dangerous interactions.
Managing Blood Pressure While Taking Generic Viagra
Monitor your blood pressure regularly, ideally before starting and then at least weekly during treatment. Keep a record of your readings to share with your doctor.
Lifestyle Changes
Maintain a healthy diet low in sodium and saturated fats. Regular exercise, aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week, is crucial. Limit alcohol consumption, as it can interact with Viagra and further affect blood pressure. Quitting smoking significantly benefits cardiovascular health and blood pressure.
Medication Management
Discuss all medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, with your doctor. Some medications can interact with Viagra and influence blood pressure. Your doctor may adjust your dosage of other medications or suggest alternatives to minimize potential interactions. Open communication is key to safe and effective medication management.
Seek Medical Attention
Report any significant changes in your blood pressure, such as dizziness, lightheadedness, or chest pain, to your doctor immediately. Prompt attention can prevent serious complications. Regular check-ups with your doctor are recommended while taking Viagra, especially if you have pre-existing cardiovascular conditions.
Hydration
Drink plenty of water throughout the day. Dehydration can impact blood pressure, and maintaining adequate hydration supports overall health.