Need a prescription for Viagra? Start by scheduling a telehealth appointment with a licensed physician specializing in men’s health. Many online platforms connect you with doctors quickly and conveniently, often within 24 hours. This allows for a private consultation from the comfort of your home.
During the consultation, honestly discuss your medical history, including any existing conditions and medications. The doctor will assess your suitability for Viagra, considering potential interactions and health risks. Be prepared to answer detailed questions about your sexual health and overall well-being. Transparency ensures accurate diagnosis and a safe treatment plan.
Once approved, your prescription can often be sent electronically to a pharmacy of your choice, eliminating the need for in-person visits. Compare pharmacy prices online to find the best value. Remember to always check that the pharmacy is legitimate and licensed before providing your personal information.
Important Note: Self-treating erectile dysfunction is risky. Always consult a medical professional before starting any new medication. They can provide personalized guidance and ensure your safety.
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.
- How to Find a Doctor to Prescribe Viagra
- Understanding Your Need for Viagra
- Erectile Dysfunction: What it Means
- When to Seek Medical Attention
- Beyond Viagra: Exploring Options
- Choosing Between Telehealth and In-Person Visits
- Finding Reputable Online Clinics
- Verify Licensing and Credentials
- Verifying Doctor Credentials and Licensing
- State Medical Boards
- National Practitioner Data Bank (NPDB)
- Physician Finder Tools
- Doctor’s Website and Profile
- Online Reviews (Use with Caution)
- Preparing for Your Consultation (Medical History, etc.)
- Discussing Your Medical History and Concerns Honestly
- Understanding Potential Side Effects and Risks
- More Serious Side Effects
- Following Up After Your Prescription
- Addressing Side Effects
- Monitoring Effectiveness
- Long-Term Management
- Considering Alternatives and Lifestyle Changes
How to Find a Doctor to Prescribe Viagra
Begin by checking your insurance provider’s website. Many insurers list doctors within their network who specialize in men’s health.
Use online search engines, specifying “urologist near me” or “men’s health clinic,” to locate nearby specialists. Filter results by insurance acceptance if necessary. Read online reviews carefully, focusing on patient experiences with prescription processes.
Consider telehealth platforms. Many offer virtual consultations with licensed doctors who can prescribe medication after reviewing your medical history and conducting a virtual examination. This option offers convenience and privacy.
If you’re comfortable, ask your primary care physician for a referral. They may know a suitable urologist or specialist already.
Remember to prepare a thorough medical history before your consultation. This helps ensure the doctor can accurately assess your suitability for Viagra and answer any questions you may have.
Once you’ve chosen a doctor, schedule an appointment. Be prepared to discuss your symptoms, medical history, and any medications you’re currently taking. Follow all instructions carefully.
Understanding Your Need for Viagra
Schedule a consultation with your doctor. Discuss your symptoms and medical history openly and honestly. This includes details about any underlying health conditions, current medications, and family history of heart disease.
Erectile Dysfunction: What it Means
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is the inability to achieve or maintain an erection firm enough for satisfactory sexual intercourse. Several factors can contribute to ED, including stress, anxiety, relationship issues, certain medications, and underlying health problems such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol. Your doctor will conduct a thorough assessment to identify the cause.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you experience consistent difficulty achieving or maintaining erections, affecting your sex life for three months or more, consult a doctor. Don’t self-diagnose or delay seeking professional help. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve your quality of life.
Beyond Viagra: Exploring Options
Viagra is one treatment option for ED. Your doctor will discuss your options based on your individual needs and health profile. These might include lifestyle changes (diet, exercise), other medications, or therapies like counseling. A collaborative approach ensures you receive the best possible care.
Choosing Between Telehealth and In-Person Visits
Prioritize telehealth if convenience and discretion are paramount. Online consultations offer easy scheduling and privacy, perfect for busy individuals. You’ll complete a medical questionnaire and video chat with a doctor for a prescription, potentially saving time and travel costs.
However, in-person visits allow for a thorough physical examination. This is particularly beneficial if you have underlying health conditions or require a more extensive assessment before receiving a prescription. Your doctor can perform a complete check-up, addressing any concerns beyond your immediate request.
Consider your comfort level with technology. Telehealth relies on reliable internet access and comfortable use of video conferencing. If you prefer a face-to-face interaction and a more traditional medical experience, an in-person appointment is likely preferable.
Factor in insurance coverage. Some plans fully cover telehealth, while others may not or may require a higher co-pay. Check your policy details before scheduling to avoid unexpected costs. In-person visits often involve standard co-pays, deductibles, or other out-of-pocket expenses.
Ultimately, the best option depends on individual circumstances. Weigh the pros and cons of each approach to determine the best fit for your needs and preferences.
Finding Reputable Online Clinics
Start your search by checking for accreditation. Look for clinics registered with organizations like the American Telemedicine Association or similar bodies in your country. This demonstrates a commitment to standards and patient safety.
Verify Licensing and Credentials
Confirm the clinic’s licensing and the doctors’ credentials. Independent verification through official state medical boards provides an extra layer of security. Read reviews from other patients on sites like Trustpilot or Google Reviews – pay close attention to both positive and negative feedback.
Check the clinic’s privacy policy. Ensure they clearly outline how they protect your personal and medical information. A secure website, indicated by “https,” is a good first sign. Look for a clear explanation of their consultation process, including how prescriptions are handled and dispensed. Avoid clinics that don’t offer transparent information.
Finally, inquire about their customer support. A reputable clinic will provide multiple ways to contact them with questions or concerns – email, phone, and live chat are all good options. A quick and helpful response indicates a commitment to patient care.
Verifying Doctor Credentials and Licensing
Always check a doctor’s license and credentials before sharing personal health information or seeking a prescription. Several resources facilitate this process.
State Medical Boards
Your first stop should be your state’s medical board website. Each state maintains a public database of licensed physicians. Enter the doctor’s name and verify their license status, specialty, and any disciplinary actions. This information is usually free and readily accessible. Look for the official government website to ensure you’re using a reliable source. Remember to use the correct state based on the doctor’s location.
- Example: For doctors licensed in California, search the Medical Board of California website.
- Tip: Note the license number; you can often use this number for future verification.
National Practitioner Data Bank (NPDB)
The NPDB is a national database containing information on malpractice payments and disciplinary actions against healthcare professionals. While you can’t directly access the full NPDB records without authorization (such as from a hospital or healthcare facility), it’s a valuable resource to be aware of. Its existence highlights the importance of investigating any potential red flags you may find during your research.
Physician Finder Tools
Many professional medical organizations maintain physician finder tools on their websites. These tools allow you to search for doctors by specialty and location. While these resources generally don’t provide details of disciplinary actions, verifying a physician’s listed credentials with a state medical board adds a layer of security.
Doctor’s Website and Profile
Examine the doctor’s website or online profile carefully. Look for clear contact information, a professional presentation, and verification of their credentials. However, never rely solely on this information. Always cross-reference with the state medical board.
Online Reviews (Use with Caution)
Online reviews can provide anecdotal evidence, but treat this information cautiously. They should not replace official verification of credentials and licensing. Focus on patterns rather than individual opinions.
- Check multiple review sites.
- Consider the number and types of reviews.
- Be wary of overwhelmingly positive or negative reviews.
Thorough verification of credentials protects your health and safety. Don’t hesitate to take the time to ensure you are working with a qualified and licensed medical professional.
Preparing for Your Consultation (Medical History, etc.)
Compile a complete list of your current medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements. This helps your doctor assess potential interactions.
Note any allergies you have, especially to medications. This is vital for your safety.
Record a detailed medical history, including past illnesses, surgeries, and hospitalizations. Be specific about dates and diagnoses.
List any family history of heart disease, high blood pressure, or stroke. This information is valuable for risk assessment.
Prepare a list of questions for your doctor. This ensures you receive all the necessary information.
| Category | Specific Information to Include |
|---|---|
| Heart Conditions | History of heart attacks, angina, murmurs, irregular heartbeat. |
| Blood Pressure | Current blood pressure readings, history of hypertension. |
| Eye Problems | History of glaucoma, macular degeneration. |
| Hearing Problems | History of hearing loss or tinnitus. |
| Other Medical Conditions | Diabetes, kidney disease, liver disease, bleeding disorders. |
Bring your insurance information. This simplifies billing procedures.
Consider bringing a friend or family member for support. Having someone else present can be helpful.
Discussing Your Medical History and Concerns Honestly
Provide complete and accurate information about your medical history. This includes past and current illnesses, surgeries, allergies, and medications you’re taking–prescription, over-the-counter, and supplements. Don’t omit anything, even if it seems insignificant. Accuracy ensures your doctor can make the safest and most informed decision.
Clearly explain your symptoms and concerns. Detail the frequency, duration, and severity of any erectile dysfunction you’re experiencing. Describe any related issues, such as low libido or pain during intercourse. Be specific; use concrete examples and avoid vague descriptions.
Discuss your lifestyle choices openly. Smoking, alcohol consumption, and drug use significantly impact your health and could affect treatment options. Your doctor needs this information to provide appropriate guidance.
Share your family medical history. Information about heart disease, high blood pressure, or diabetes in your family can be crucial, as these conditions increase the risk of certain complications.
Ask questions! Don’t hesitate to ask your doctor about potential side effects, alternative treatments, or anything else you’re unsure about. An open dialogue ensures you understand the plan and feel comfortable with your choice.
Prepare a list of your questions beforehand. This ensures you remember to address all your concerns during your consultation. Bringing this list facilitates a productive conversation.
Trust your instincts. If you feel uncomfortable or unsure about any aspect of your consultation, speak up. A good doctor-patient relationship is built on mutual trust and open communication.
Understanding Potential Side Effects and Risks
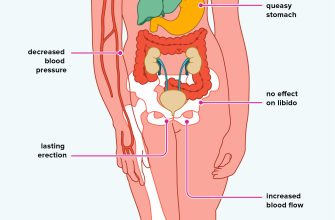
Viagra, while effective for many, carries potential side effects. Common ones include headache, facial flushing, nasal congestion, and upset stomach. These usually are mild and temporary.
More Serious Side Effects
Less common, but more serious, side effects require immediate medical attention. These include chest pain, sudden vision loss or hearing loss, prolonged erection (priapism), and allergic reactions (such as rash, swelling, or difficulty breathing). Seek immediate medical help if you experience any of these.
Certain pre-existing conditions increase the risk of side effects. Men with heart problems, low blood pressure, or liver/kidney disease should discuss Viagra use with their doctor. Also, combining Viagra with nitrates (found in some heart medications) can be dangerous, potentially leading to a significant drop in blood pressure.
Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely regarding dosage and frequency. Open communication with your doctor is key to mitigating risks and ensuring safe and effective use.
Following Up After Your Prescription
Schedule a follow-up appointment with your doctor within a month to discuss your experience with Viagra. This allows you to report any side effects or address any concerns you may have.
Addressing Side Effects
Minor side effects, such as headaches or flushing, often subside. However, persistent or severe side effects, like chest pain or sudden vision changes, require immediate medical attention. Contact your doctor immediately if you experience anything concerning.
Monitoring Effectiveness
During your follow-up, honestly discuss the medication’s effectiveness. If Viagra isn’t working as expected, your doctor can adjust the dosage or explore alternative treatment options. Open communication is key to finding the right solution for you. Your doctor might suggest lifestyle changes or additional tests to rule out underlying health issues affecting your erectile function.
Long-Term Management
Regular check-ups are important for long-term management. These appointments allow for ongoing monitoring of your health and ensure the continued effectiveness and safety of your treatment plan. Don’t hesitate to ask questions – your doctor is there to support you.
Considering Alternatives and Lifestyle Changes
Before seeking medication, explore natural remedies. Regular exercise, at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity activity per week, significantly improves cardiovascular health, often addressing erectile dysfunction’s root causes.
Dietary changes are also crucial. Focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Limit processed foods, saturated fats, and excessive sugar intake. A diet high in antioxidants, found in berries and leafy greens, supports blood vessel health.
- Consider adding zinc-rich foods like oysters, pumpkin seeds, and lentils to your diet. Zinc plays a role in testosterone production.
- Increase your intake of L-arginine, an amino acid that helps relax blood vessels. Good sources include nuts, seeds, and red meat (in moderation).
Manage stress effectively. Chronic stress significantly impacts sexual function. Incorporate relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises into your routine. Aim for at least 30 minutes of relaxation daily.
Address underlying medical conditions. Erectile dysfunction can be a symptom of other health problems, including diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol. Managing these conditions can improve erectile function. Consult your doctor for a comprehensive health assessment.
- Quit smoking. Smoking damages blood vessels, negatively affecting blood flow to the penis.
- Limit alcohol consumption. Excessive alcohol use can impair sexual function.
- Maintain a healthy weight. Obesity is linked to a higher risk of erectile dysfunction.
These lifestyle modifications can significantly improve erectile function for many men. If these changes are insufficient, then consult a doctor to discuss other treatment options.